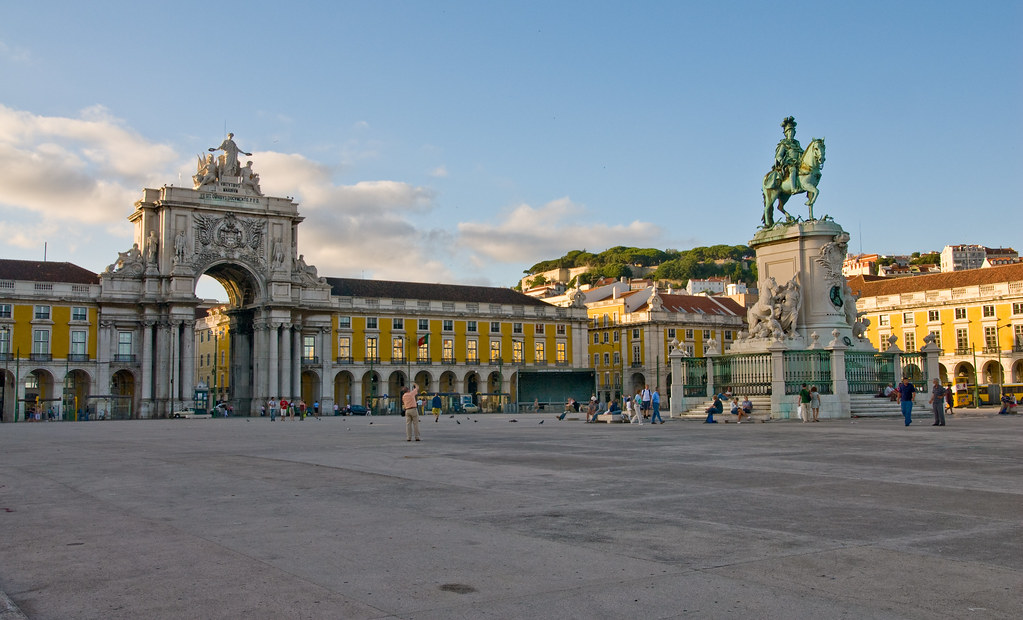
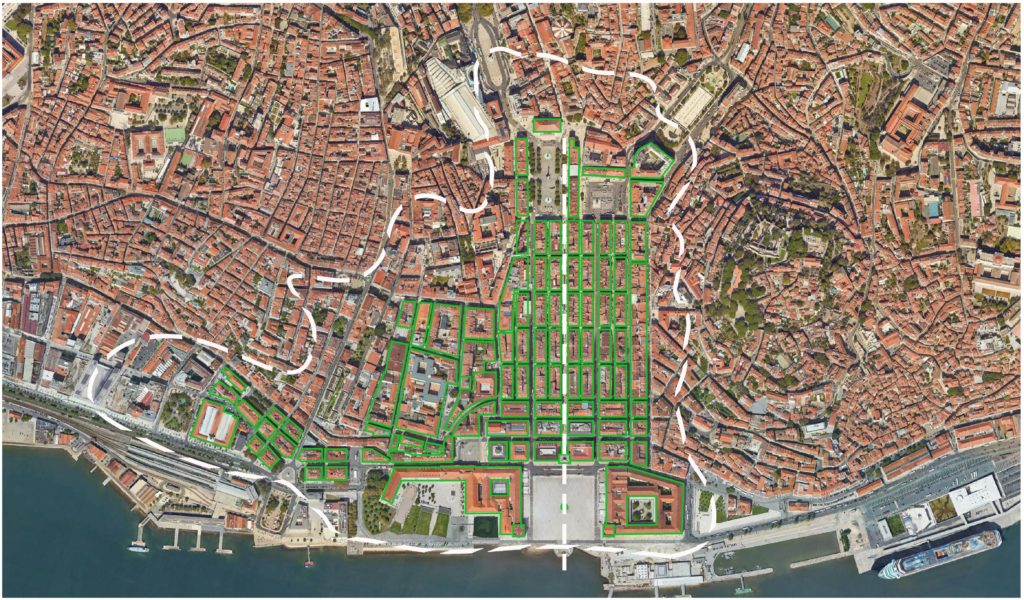
The Pombaline style of architecture refers to a distinctive architectural style that emerged during the reign of Marquis of Pombal, Sebastião José de Carvalho e Melo, who was the Prime Minister of Portugal from 1750 to 1777. This architectural style is primarily associated with the reconstruction efforts that took place in Lisbon after the devastating earthquake of 1755.
The Pombaline style is characterized by its rational and utilitarian approach, influenced by the Enlightenment ideas of the time. It was a response to the need for a quick and efficient reconstruction of the city, focusing on durability, safety, and functionality. Some key features of the Pombaline style include:
- Earthquake-resistant construction: The style is known for its innovative building techniques aimed at mitigating the impact of future earthquakes. The buildings were designed with a grid system and sturdy masonry walls, often reinforced with timber frames or iron bars. This allowed for greater stability and flexibility during seismic activity.
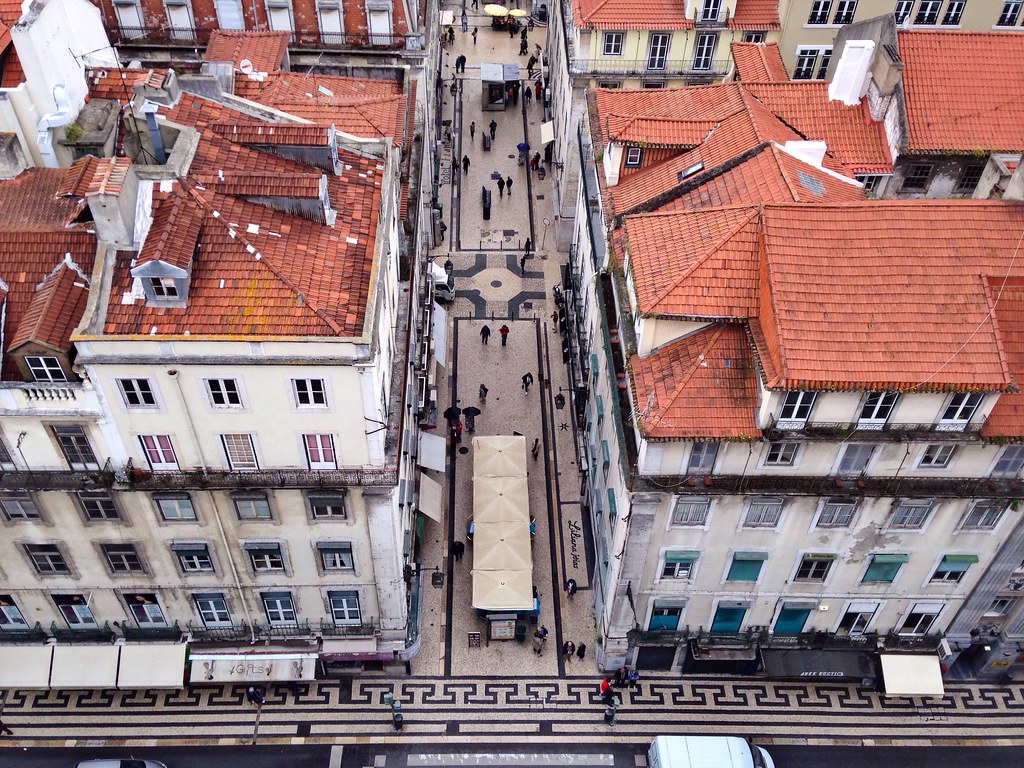
- Uniformity and order: The Pombaline style emphasized a uniform and organized urban layout. The streets were straightened, widened, and aligned to facilitate traffic flow and improve accessibility. The buildings were constructed in a grid pattern, creating a sense of order and symmetry throughout the city.
- Simple and austere facades: The facades of Pombaline buildings are typically characterized by simplicity and restraint. Ornamentation was kept to a minimum, and the focus was on functionality rather than decorative elements. The buildings often featured balconies with wrought iron railings and large windows to allow for natural light and ventilation.
- Mixed-use buildings: The Pombaline style promoted mixed-use buildings, incorporating residential, commercial, and public spaces within the same structure. This approach aimed to maximize the efficient use of space and create a vibrant and dynamic urban environment.
Overall, the Pombaline style of architecture represents a significant shift in urban planning and building construction techniques. Its emphasis on earthquake-resistant design and rational urban layout had a lasting impact on the development of Lisbon and influenced architectural trends in Portugal and beyond. Today, many Pombaline buildings can still be found in Lisbon, serving as a testament to the resilience and innovation of this architectural style.


Other architectural styles
Gothic Architecture
Gothic architecture is a style of architecture that emerged in Europe during the late medieval period, spanning from the 12th to the 16th centuries. It is characterized by several distinctive features that set it apart from other architectural styles of its time. Here are the key features of Gothic architecture: Gothic architecture represented a departure…
Baroque Architecture
Baroque architecture is an extravagant and theatrical style that emerged in Europe during the late 16th century and flourished until the early 18th century. It is characterized by grandeur, ornate decoration, and a sense of motion and drama. Here are some key characteristics of Baroque architecture: Overall, Baroque architecture is a style that revels in…
Rococo Architecture
The Rococo style of architecture emerged in the 18th century as a continuation of the Baroque style, but with a lighter and more delicate aesthetic. It originated in France and spread throughout Europe, particularly in countries such as Germany, Austria, and Italy. Rococo architecture is characterized by its emphasis on asymmetry, ornate decoration, and a…
Neoclassical Architecture
Neoclassical architecture is a style that emerged in the mid-18th century as a reaction against the extravagance and complexity of the Baroque and Rococo styles. Inspired by the classical architecture of ancient Greece and Rome, neoclassical buildings sought to revive the principles and aesthetics of classical antiquity while incorporating a sense of order, simplicity, and…
Renaissance Architecture
Renaissance architecture refers to the architectural style that emerged in Europe during the Renaissance period, roughly spanning from the 14th to the 17th century. This style was a revival and reinterpretation of the classical architectural principles of ancient Greece and Rome. Here are some key features of Renaissance architecture: These features collectively contributed to the…
Romanesque Architecture
Romanesque architecture is a medieval architectural style that flourished in Europe from the 10th to the 12th century. It was a distinctive architectural form that evolved from the earlier Roman and Byzantine architectural traditions and laid the foundation for the Gothic style that followed. Here are the key characteristics of Romanesque architecture: Overall, Romanesque architecture…
Moorish Architecture
Moorish architecture refers to the architectural style that developed in the Western Islamic world during the period of Moorish rule (8th to 15th centuries) in Spain, North Africa, and parts of Portugal. It is known for its unique and distinctive characteristics. Here are some key features of Moorish architecture: These characteristics collectively contribute to the…
Pombaline Architecture
The Pombaline style of architecture refers to a distinctive architectural style that emerged during the reign of Marquis of Pombal, Sebastião José de Carvalho e Melo, who was the Prime Minister of Portugal from 1750 to 1777. This architectural style is primarily associated with the reconstruction efforts that took place in Lisbon after the devastating…
Manueline Architecture
The Manueline style of architecture in Portugal is a unique and ornate architectural style that emerged during the late 15th and early 16th centuries, coinciding with the Age of Discovery when Portugal was at the forefront of maritime exploration and trade. Named after King Manuel I of Portugal, who ruled during this period, Manueline architecture…
Art Deco Architecture
Art Deco architecture is a distinctive architectural style that emerged in the early 20th century, reaching its peak in the 1920s and 1930s. It is characterized by its bold geometric shapes, streamlined forms, and luxurious decorative elements. Here are the key characteristics of Art Deco architecture: Overall, Art Deco architecture is characterized by its boldness,…
Art Nouveau Architecture
Art Nouveau, also known as “New Art” or “Jugendstil,” was an influential art movement that emerged in the late 19th century and flourished until the early 20th century. It was an international style that manifested in various art forms, including architecture, decorative arts, and graphic design. Art Nouveau architecture sought to break away from the…









You must be logged in to post a comment.