The saguaro cactus (Carnegiea gigantea) is an iconic symbol of the Sonoran Desert and is one of the largest and most recognizable cacti in the world. Here are some key features and characteristics of the saguaro cactus:
Appearance:
Size: Saguaros are typically tall and columnar, with mature specimens reaching heights of up to 40 feet (12 meters) or more.
Shape: They have a classic candelabra-like shape with a main trunk and multiple upward-arching arms (branches). These arms typically begin to grow once the saguaro reaches 75 to 100 years of age.
Ribs: The saguaro’s stem has prominent vertical ribs that can expand to allow for water storage during rainy periods. These ribs also help the cactus expand and contract as it stores and uses water.
Spines: The surface of the saguaro is covered with sharp spines that help protect it from herbivores and regulate surface temperature by reducing solar radiation absorption.
Habitat and Distribution:
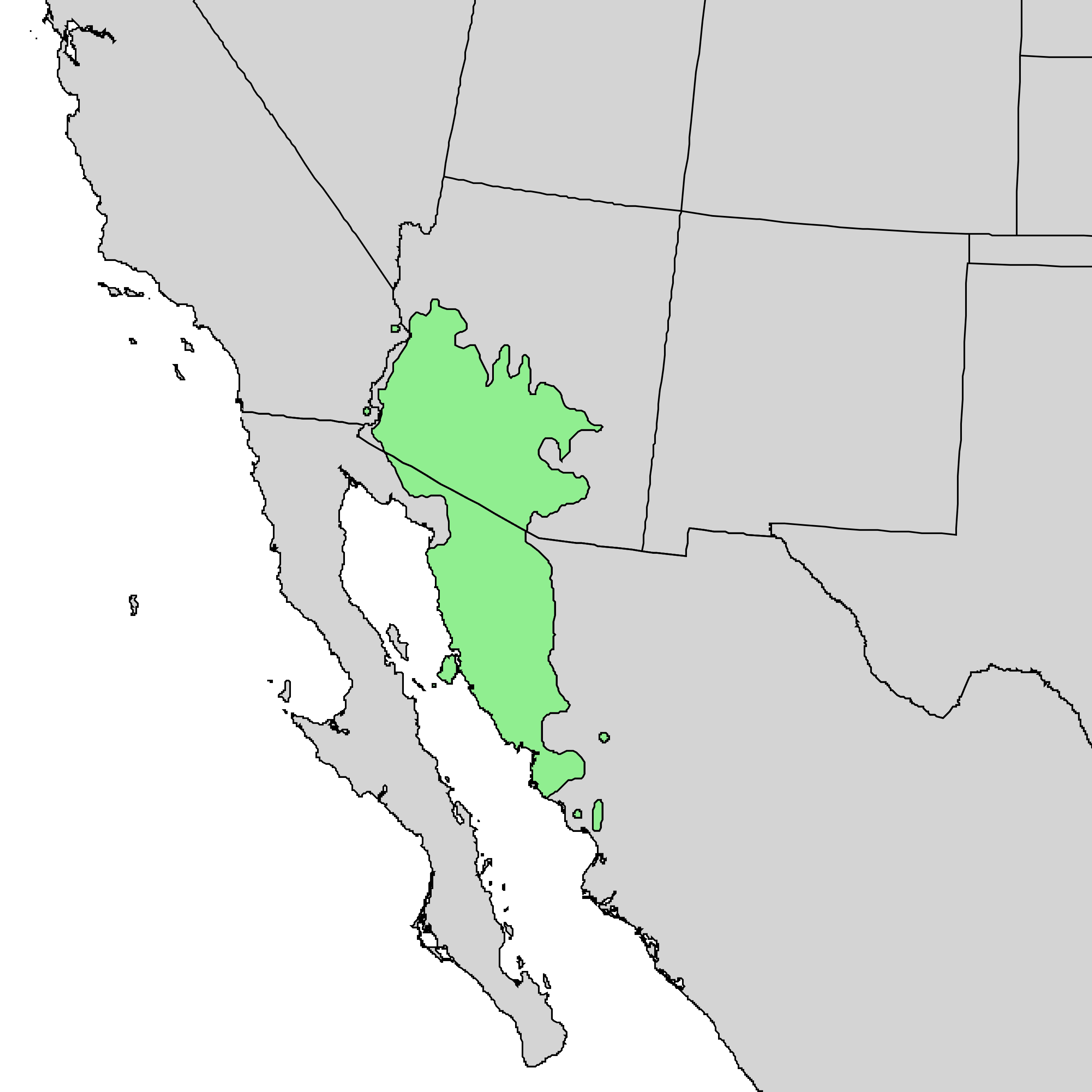
Range: Saguaros are native to the Sonoran Desert in Arizona, southeastern California, and northwestern Mexico.
Habitat: They typically grow in rocky, well-drained soils on desert hillsides and flats. Saguaros require full sun exposure and are often found at elevations ranging from sea level to around 4,000 feet (1,200 meters).
Life Cycle and Growth:
Growth Rate: Saguaros are slow-growing cacti, taking up to 75 years to develop a height of about 6 feet (1.8 meters).
Flowering: They bloom in late spring to early summer, producing large, white flowers with a diameter of about 3 inches (8 cm). These flowers open during the cooler hours of the evening and are pollinated by bats, birds, and insects.
Fruit: The fruits are red and contain many tiny black seeds. They are an important food source for desert wildlife, including birds like the Gila woodpecker and mammals like the desert packrat.
Ecological Importance:
Wildlife Habitat: Saguaros provide nesting sites for birds and shelter for various desert animals, contributing significantly to desert biodiversity.
Water Storage: Their ability to store large amounts of water allows them to survive long periods of drought, making them a keystone species in their ecosystem.
Cultural Significance:
Symbolism: Saguaros hold cultural significance among indigenous peoples of the Sonoran Desert, who have used them for food, shelter, and ceremonial purposes for centuries.
Protection: The saguaro is protected under state and federal laws in the United States to prevent vandalism and ensure their preservation.
The saguaro cactus is not only an iconic symbol of the Sonoran Desert but also a vital component of its ecosystem, providing habitat, food, and shade to a wide variety of desert wildlife. Its unique appearance and adaptations make it a fascinating example of how plants thrive in arid environments.






